The Vagina - Types of Vaginal Discharge - Vaginal infection
The vagina is a sex organ that is derivative of the embryonal Mullerian duct. It consists of fibromuscular tissue and it extends from the vulva to the uterus, its opening is protected by the labia. The vagina is lined with stratified squamous epithelium and its inner mould has a foldy texture that creates friction during intercourse. And there is a smooth muscle layer below the vaginal lining that contract during labor and also during sexual intercourse. The length of the vagina for a woman of childbearing age is 6.0 to 7.5 cm anteriorly and 9 cm posteriorly. During sex, the vagina expands in dimension.
The membrane of the vaginal wall produces secretions although it doesn’t have glands. The bartholin glands also produce vaginal lubrication and it is located near the vaginal opening and the cervix. During ovulation, an alkaline environment is needed in the vagina for the survival of the sperm, and this is provided by the alkaline mucus that is produced by the cervix mucus glands. Normally, as a woman's age increases, the vaginal lubrication decrease,s and after menopause, a thinning occurs in the vaginal wall due to the decrease in the amount of estrogen in the body.
The Hymen is a membrane that partially covers the opening of the external vagina. And the effect of sexual intercourse on it is variable. If its elasticity was sufficient, it may return to its original shape, or it may disappear completely after repeated penetration.
Functions of the vagina:
- It is a path for passage of uterine secretions such as menstrual blood, to exit the body.
- The vagina stretches during child birth due to its elasticity and this creates a channel for the passage of the newborn outside the uterus. That is why the vagina is called the birth canal.
- It receive the penis during sexual intercourse.
- - The lower third of the vagina, especially near the opening, contains nerve endings that cause the pleasure sensation during sexual intercourse. However, the other parts of the vagina have insufficient nerve endings to make the childbirth less painful.
- When arousal sensations have been achieved, lubrication will be produced in the walls of the vagina that will reduce the friction that may happen during intercourse. And with arousal, the vagina expands especially its last 2/3rd in length and width, and the vagina will stretch to accommodate the size of the penis. This will stimulate the penis to result in orgasm and ejaculation which hopefully leads to fertilization.
- G-spot (grafenberg spot) is located about 5 centimeters from the vaginal entrance in the anterior wall. And if it is stimulated, it will cause intense pleasure and may lead to female orgasm and ejaculation.
Erogenous Zones Video | Male reproductive system Video | Response To a Sexual Stimulus Video | Female reproductive system Video
Types of Vaginal Discharge:
Normal Vaginal Discharge:
These are usually related to menstrual cycle and to the ovulation, the cyclic discharge (that occurs at the beginning and end of cycle) is normal and it is usually thick, white and odorless. And a clear stretchy discharge occurs normally at the time of ovulation.
The vagina contains bacteria such L-acidophilus and L.doderlein that produce lactic acid from glycogen. This is responsible for the acidity of the vagina.
The bartholin gland that is located in the vagina secretes mucus which lubricates the vagina.

Abnormal Vaginal Discharge
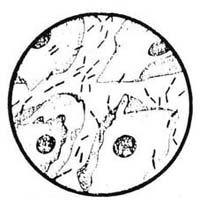
Normal Vaginal Discharge
Abnormal Vaginal Discharge:
- Thick, white and clumpy discharge is caused by fungal infection (candidiasis) and it is associated with itching, swelling, and pain.
- Bloody or brown discharge is associated with irregular menstrual cycle.
- Yellow or cloudy discharge is caused by Gonorrhea infection and it is usually associated with urinary incontinence.
- Trichomoniasis is associated with frothy, yellow and greenish discharge with a very bad smell and it is associated with itchiness and painful urination. Bacterial vaginosis
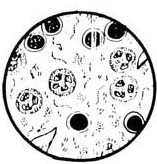
- Bacterial vaginosis is associated with yellow, gray, or white discharge with a fishy odor. It produces itching, burning, and redness of the vagina.

Trichomoniasis
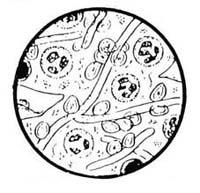
fungal infection
- Cysto-vaginal fistula causes passage of urine from the vagina.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding may be caused by:
- - Dysfunction of hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland or the ovaries.
- Postmenopausal bleeding that may result from endometrial hyperplasia or fibroids.
- Bleeding disorders.
- Chronic, severe inflammation.
- Benign and malignant tumors.
- Stress.
- Vitamin deficiencies.
- Puberty.
- Vaginal injuries by chemicals or foreign bodies.
Factors which increase risk of Vaginal Infection:
- Cold exposure.
- Sexually transmitted diseases (trichomoniasis, syphilis, gonorrhea).
- Poor hygiene.
- Recurrent urinary tract infections.
- Prolonged use of antibiotics and exposure to chemotherapy.
Types of Vaginal Inflammation (Vaginitis):
- Vaginal and urinary tract infection. It is usually transmitted by sexual intercourse (gonorrhea, bacteria, trichomoniasis, etc)
- Atrophic vaginitis: Caused by the decrease of estrogen which happens in post menopausal women and will lead to thinning and atrophy of vaginal tissues, and to dryness. This will cause symptoms such as itching, burning, whitish discharge, and painful sexual intercourse.
- Fungal infection: This increases in pregnant women, in diabetics, in users of combined oral contraceptive pills and it increases after taking an antibiotic which will kill the vaginal bacteria that transform glycogen to acids.
- Vaginal diphtheria.
- Inflammation of vaginal erosions that may result from injuries by foreign bodies or chemicals or by ulcers that is associated with Behçet's disease.
Diagnoses of Vaginal Infection:
The best way is to go to the doctor to take a sample from the discharge for culture. A Pap smear may be taken by collecting cervical cells.
Tips to avoid Vaginal Infections:
- Clean the infected area with water and medical soap three times daily and then dry the area and leave it exposed for 30 minutes.
- Use the cream that is prescribed by the doctor after washing the infected area and keep it exposed for 30 minutes.
- When using the vaginal ovules, you have to insert it as far as you can inside the vagina and it is preferred to be used before going to sleep.
- Avoid nylon underwear. Cotton underwear is preferred.
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
