Causes of male infertility
1-Causes that are related to the glands controlling testicular function:
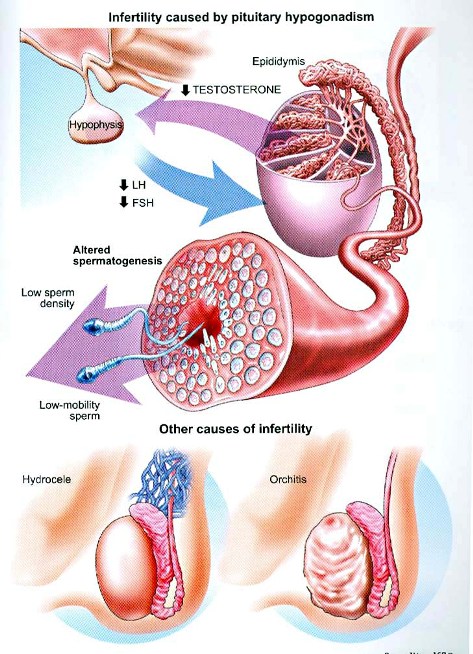
- Delayed puberty.
- LH, and FSH deficiency.
- Congenital hypo-gonadotrophic hypogonadism (deficiency of pituitary gland hormones) e.g.: Kallman’s syndrome which is associated with abnormal sense of smelling.
- Other causes that may result in destruction of pituitary and hypothalamic glands are
- trauma
- irradiation
- tumors
- medications
- surgery.
-
Hyperprolactinemia due to pituitary adenoma or a side effect(s) of some medications.
Measurement of these hormones (LH, FSH, prolactine, and testosterone) will help in the diagnosis, for example:
- Primary testicular failure is associated with low testosterone level, and high LH, FSH. This syndrome is associated with either low sperm count (oligospermia) or completes absence of sperms (azoospermia).
- Retrograde ejaculation, if there is an obstruction in ejaculatory ducts, or germinal cell failure in these situations there will be normal levels of testosterone, LH and FSH.
-
Dans le manque de récepteur LH :
In this case, though hormonal levels are normal, but they are ineffective.
- If all of these hormones are low, it might be associated with other hormonal deficiencies, such as low growth hormone, low corticotrophin, low TSH.
Depending on these levels the treating physician, might determine the cause.
2-Testicular Disorders
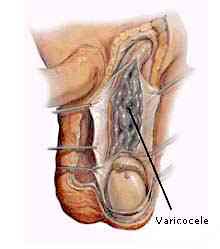
- Idiopathic causes for testicular problems.
- Congenital causes.
- Chromosomal causes such as, klinefelter’s Syndrome (47XXY).
- Undescended testis or (cryptochidism) that may cause harm to testicular tissue.
- Congenital absence of both testes.
- Testicular varicocele : This is usually diagnosed through a physical examination, and using ultrasound, in this case tortuous veins around the epididymis, this might affect sperm production, and quality, but varicocele effect is still under debate, and there is controversy among researchers, and doctors as to whether it has a major effect or not.
- Major trauma to the testes.
- Severe testicular infection.
- Testicular tumors.
- Hazardous chemical or physical exposure.
- Medications such as cyclosporine, allopurinol, colchicines, sulfasalazine, spiranolactone.
- Drugs such as marijuana and alcohol especially if there is an addiction, will affect sperm quality, and slow its motility.
- Some chemicals used in factories like nematocid DBCP, lead, and mercury affects sperm production.
- Chemotherapy that is used in the treatment of cancer patients.
All the above mentioned points affect sperm production or even might cause spermatogenesis arrest.
- Smoking.
It is well known that smoking has effects on sperm production, motility, and morphology some researchers found that smokers who have varicocele have less ability for sperm production five times less as compared to nonsmokers.
- Heat has a major role in sperm production, so men should avoid wearing tight underwear for long periods, as it may cause low or reduced sperm count.
- Jobs that require sitting for long times, may affect sperm count.
- Chronic medical illnesses, such as chronic renal failure, or chronic liver failure.
- Immunological disorders: It may cause sperm antibodies that will kill the sperm.
3-Disorders related to epididymis, seminal vesicles, and prostate:
- Congenital causes: Vas aplasia, malformation of caudal corpus epididymis.
- Congenital obstruction of seminal vesicles.
- Congenital obstruction associated with bronchial dilatation of the lungs.
- Severe infections may cause epididymal obstruction: Some of the Microorganisms that may also cause infections are staph, gonorrhea tuberculosis, trachoma, anaerobes and Chlamydia.
- Vasectomy: A procedure done for male contraception in this procedure a cut in seminal ducts is done which will cause male infertility.
4-Coital Defects
- Inappropriate time for intercourse (not at time of ovulation).
- Erectile dysfunction: It could be due to psychological, neurological or vascular disorders or as a side effect for some medication.
- Using certain ointments or creams at the time of intercourse, some of which may kill the sperm.
- Hypospadias: This means abnormal position of urethral meatus.
- Congenital Penile Defects.
- Retrograde ejaculation: In these patients the semen flows to the bladder at the time of ejaculation instead of out through external opening this happens when there is a problem in bladder neck due to:
A-Congenital causes:
- Stenosis of the external urethra.
- Stenosis of the external valve due to hypertonic muscles.
- Congenital anomaly of the internal valve.
- Congenital stenosis of bladder neck.
B-Acquired cause:
- Neurological injury due to spinal cord injury.
- Pelvic fractue.
- Pelvic surgery.
- Diabetes.
- Prostate surgery.
- Bladder surgery.
- Urethral dilatation.
C-Unknown causes.
5-Abnormal semen:
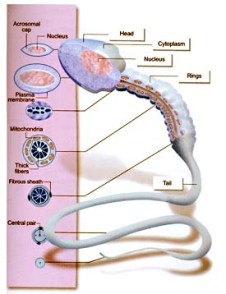
- Disorder of the sperm and its ability to fertilize.
- Immotile cilia syndrome.
- Necrospermia (dead sperm).
- Periaxonemal abnormalities.
- Increase viscosity of the semen above the normal levels.
- Some factors that may suppress the sperm such as deficiency of certain enzyme, which is important in sperm motility (protein- carboxyl methylase PCM).
- Zinc deficiency.
- Decrease the amount of the substances needed for sperm motility or decrease their use by the sperm (Adenosine triphosphate A.T.P).
- Sperm membrane malformation.
- Disorders in calcium metabolism.
- Lack of the substances in the semen that are needed for sperm motility such as bicarbonate or abnormal levels of prostaglandins.
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
