Causes of Infertility in Women
Definition of infertility: Inability to conceive despite trying and having regular intercourse for one year.
Infertility is one of the widespread problems facing couples. And the causes could be due to female factors or male factors.
Female factors:
It has been proven by multiple researchers that the ability for women to conceive decreases with increasing age.
1- Vaginal Causes of Infertility in Women
Blockage of the vagina which will interfere with the entrance of the male organ such as imperforate hymen, or extremely narrow vagina, or painful infections in the vagina.
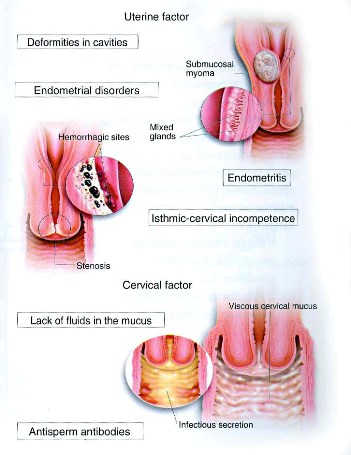
2- Cervical Causes of Infertility in Women
- Previous cone biopsy or laser conization. This might cause a decreased amount of mucous. This will affect sperm movement.
- Presence of anti-sperm antibodies.
- Closed cervix (very rare condition).
3- Uterine Causes of Infertility in Women
-
a. Congenital anomalies: Most of them precipitate from abortions, but some of them affect fertility and can be corrected surgically, such as a septate or divided uterus, which can be removed by
hysteroscopy. Anomalies such as bicornuate uterus, rudimentary horn and T-shaped uterus.
These anomalies usually are associated with unilateral or bilateral fallopian tube anomalies so they will also increase the risk for ectopic pregnancy and recurrent pregnancy loss in addition to infertility.
- b. Asherman Syndrome:In this syndrome intra uterine adhesions form either after repeated curettage, severe endometritis, or due to scars from previous uterine surgery. Women with this syndrome usually complain of decreased amount of blood loss during menstruation. It can be diagnosed easily using hysterosalpingogram. And hysteroscopic resection of these adhesions can be done but it may need multiple sessions, in addition to giving steroids with estrogen for three weeks after surgery to avoid recurrence.
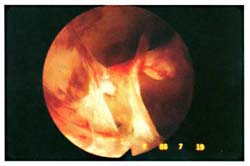
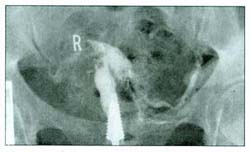
Asherman Syndrome
-
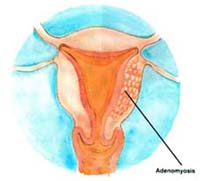
c. Fibroids:Fibroids are a benign uterine tumor that might cause irregularities in the intrauterine cavity.Adenomyosis They usually do not cause infertility unless it affects the intrauterine cavity in an obvious way, but if no other reason for infertility can be found, it is better to do myomectomy (excision of the fibroid ) and restore the intrauterine cavity. Myomectomy can be done either by hysteroscopic resection or by laparatomy (abdominal incision is done to access the abdominal cavity then removal of the fibroid is done).
- d. Fibrosis:This may happen after endometritis and can be diagnosed using HSG, hysteroscopy can help in treatment.
- e. Endometrial polyp:Its presence mimics IUCD, polyps can be diagnosed by HSG, ultrasound or hysteroscopy then polypectomy (removing the polyp) can be done easily.
- f. Adenomyosis:Symptoms include secondary dysmenorrhea, some hormonal treatments could be helpful e.g. GNRH analogues, or Danazol, the decision for this treatment should be taken by the treating physician.
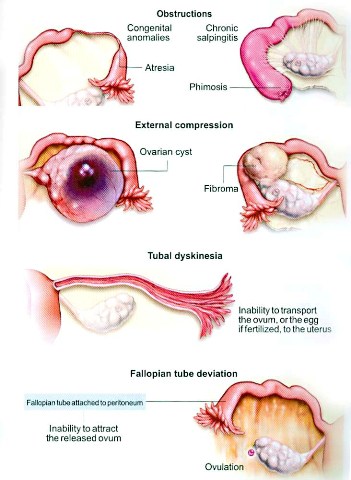
4- Tubal factors causing Infertility in Women:
-
a. Chronic pelvic infections: This problem will cause tubal congestion. If the cross section reaches more than 3cm, tubal obstruction results in impeding of the oocyte transfer, chronic pelvic infections may also result in pelvic adhesions that will affect tubal movement. Slowing it so inappropriate time for oocyte transfer interferes with fertilization. Pelvic inflammatory disease will result in tubal occlusion or pelvic adhesions that cause inability for the fimbrial ends to catch the oocyte from the ovary or as mentioned before abnormal movement of the tubes and oocyte transfer. Causes for PID include infections with E.coli, or Gonococcus infection (STD) PID affects ovarian function and tubal movement. And it may be severe enough to destruct the tubes requiring surgical resection.
- - b. Destruction of the fimbrial ends :Disabling its function in catching oocytes into the tubes, PID or endometriosis can cause this.
- - c. Adhesions: Caused by tubal surgery done for ectopic pregnancy, pelvic surgery done to the tubes or due to appendicitis.
- - d. Short tubes(less than 4cm).
- - e Tubal Tumorsaffecting it's function.
5- Ovarian dysfunction:
-
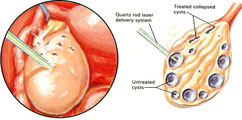
- A. Polycystic ovarian disease: 20% of females have what is called polycystic ovary which involves having follicles consisting of more than the normal condition.Ovarian Drilling In this case the woman has normal fertility but if it is associated with some of the following conditions, it is called polycystic ovarian syndrome and it is pathological. Please press on the link to read more about Polycystic ovarian disease.
What about the possibility of doing IVF for these women?
IVF was first done for women who have tubal occlusion or male abnormal semen analysis.
But the decision, whether women with PCOD will need IVF, should be individualized as said earlier.
-For hirsuitism treatment for women, seeking pregnancy is different from those who are not.
Most of the time, treatment of hormonal imbalance is the best thing.
-Regarding recurrent abortions in PCO patients, it occurs due to a slightly increased LH level, so it’s better to give medications to manage its level before starting induction of ovulation. Also some researchers have shown that ovarian diathermy lowers LH level and consequently lower the incidence of recurrent miscarriages.
-
B- Failure of the ovary to perform its normal function:
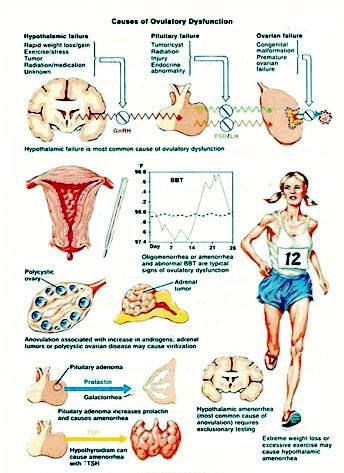
- 1- Ovarian failure :
- A- Congenital causes.
1- Genetic and chromosomal causes.
- Ovarian agenesis.
- Hereditary causes for accelerated loss of ovarian reserve.
- Familial premature ovarian failure.
- Chromosomal abnormalities (47XXX).
2- Congenital enzymatic dysfunction.
- 17-α Hydroxylase Deficiency.
- Galactosemia.
B- Exposure to certain factors:
- Large amount of radiation exposure.
- Chemotherapeutic agents as in cancer treatment.
- Viruses such as mumps.
- Heavy smoking.
C- Autoimmune causes: Presence of ovarian antibodies.
D- Lack of (or dysfunction) of LH, FSH ovarian receptors.
E- Idiopathic causes.
F- Surgical oopherectomy.
- A- Congenital causes.
- 2- Physiological ovarian failure. Such as corpus luteum insufficiency or luteal unruptured follicle.
- 1- Ovarian failure :
-
C- Pituitary failure:
- 1- Secondary disorder of Gonadotrophin Regulation. High prolactine level either due to pituitary adenoma, idiopathic hypothyroidism or as a side effect to medication, which affects follicular maturation.
- Suprapituitary Tumors,.
- Pituitary Tumors, trauma such as in RTA, radiation exposure to the pituitary.
- Idiopathic causes.
2- LH and FSH gonadotrophin Deficiency due to:
- Pituitary tumors.
- Destructive pituitary lesion.
- Pituitary ablation.
- 1- Secondary disorder of Gonadotrophin Regulation. High prolactine level either due to pituitary adenoma, idiopathic hypothyroidism or as a side effect to medication, which affects follicular maturation.
-
D- Hypothalamic failure.Which could be as a result of:
- Rapid and sudden increase or decrease in body weight.
- Severe psychological and neurological stress strenuous exercises.
- Radiation exposure.
- Medications that cause hypothalamic failure.
- Tumors.
- Unknown causes.
-
E- Endocrinopathy
Such as *Adrenal gland dysfunction which lead to hyperandrogenic state.
*Thyroid gland problems.
Hypothyrodism causes hyperprolactinemia and hyperthyroidism affects hormones necessary for follicular maturation, pancreatic problems such as diabetes.
6- Endometriosis:
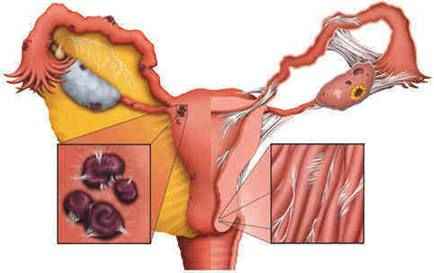
Which is the presence of endometrial tissues outside endometrial cavity it affects pregnancy either by forming chocolate cyst (or endometrioma) or by causing adhesions. Please press on the link to read more about Endometriosis
Diagnosis is usually done by laparoscopy and treatment includes laparoscopic adhesiolysis, cauterization of endometriotic spots, salpingostomy and reanastomosis of fallopian tube problems.
Success rate of tubal dilatation is around 35%, and if it was cornular obstruction (the area where the tube is connected to the uterus) success rate is around 55-60% success rate and can reach 80% in cases of tubal reconstruction.
Cornular Dilatation is done by passing a special tube through the cervix to the tube.
In cases of ovarian cysts (hemorrhagic cyst) surgical intervention is needed. Treatment of chronic PID causing adhesions, is similar to treatment of endometriosis, that is adhesiolysis and tubal reconstruction.
7- Unexplained Infertility:
Inability to conceive after two years of marriage despite having regular intercourse, multiple researches have been done with multiple theories attempting to explain it.
- Presence of certain amounts of fatty acids in the sperm
- Cervical leucocytosis.
- Psychological causes.
It is said that stress and strenuous exercise, and unstable changes in weather may cause oligospermia but there is lack of strong evidence for this. But, psychological causes might affects premature ejaculation or erectile dysfunction. The best psychological support for the male is from his wife regarding psychological causes. In women, it affects sexual function and ovulatory failure. In our society, most females, after marriage, will find problems in proper sexual intercourse that is related to the way that most of them are raised, and psychotherapy is helpful in these cases.
- Some hypotheses say that stress and worries may cause significant changes in internal hormones such as decreased cervical secretions or muscular spasm, including those lining fallopian tubes causing its obstruction, or muscles lining the vagina causing dyspareunia.
Stress also has its effects on the hypothalamus and ovarian function.
So we advise each couple seeking pregnancy to try, as much as possible, to alleviate stress and worries as much as possible and have trust in god and trust their treating physician.
- Genetic causes.
- Endometrial Immunity.
- Lack of some vitamins and ferritine level.
It should be said that these causes are rare and not that familiar, researchers are doing their best to identify and treat these causes.
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
