Diagnosis of Infertility in Men | Diagnosis of male infertility
Diagnosis of Infertility In Men

A-Medical history:
Taking detailed medical history from both couples, they should be asked if there is any medical illness such as: Diabetes, high fever, taking certain medications for long times, mumps, any previous genital disease, any previous surgical intervention especially concerning the female pelvis and genitourinary system for the male, delay in pregnancy, previous miscarriages, previous marriages and if they had pregnancy in these marriages, frequency of intercourse, age of puberty, previous history of exposure to chemotherapy, irradiation or very high temperature. In addition to many other questions that may help to diagnose the causes for infertility.
B-Physical examination:
General examination is done at the beginning (head, neck, chest, abdomen, upper and lower limbs), then concentrate more on the examination of genital area.
C-Diagnostic procedures and tests:
1-Seminal fluid analysis
It should be emphasized here that one abnormal test is not enough to judge that there is abnormality in the semen. Most of the time, it should be repeated 2-3 times because many factors (such as his medical condition) affects the semen.
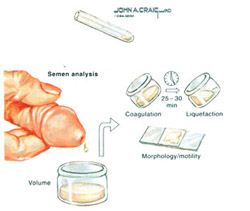
The following instructions should be followed before doing SFA:
- Abstinence for 3-5 days.
- Avoid taking hot shower before giving the sample.
- Wash your hands with soap, then by water.
- Washing the genital area several times.
- Make sure to close the collecting tube carefully, and not to lose any amount from the sample given.
- The time between giving the sample and bringing it to the lab shouldn’t exceed one hour, it should be kept in the palm of hand or in close contact to the body to maintain its temperature around 37c.
2-Evaluation of the ability of sperms to fertilize:
Seminal fluid analysis doesn’t evaluate functional ability of the sperm so many tests were developed:
a-Testing the ability of the sperm to move inside the female body.
-Post coital test (it will be explained later).
-In-vitro mucous penetration test (ability of sperm to pass through cervical mucus).
-Sperm survival tests (the ability of the sperm to move at some point of time within a certain perimeter).
b-Acrosome reaction:This is done by using certain dye for the sperms to identify the presence of acrosome and its functional ability.
c-Hyposmotic swelling test:
This test identity the percentage of sperms with healthy membrane, and its ability.
d-Ability of the sperm to inject the oocyte:
-Hamster ovum penetration test.
-Hemizona assay.
-In-vitro fertilization of human oocyte.
3-Immunity tests:
The presence of antis perms antibodies through blood tests or semen plasma or the sperms.
4-Microbiological tests:
It is done when there is genital tract infection or if there is high level of white blood cells in the semen.
5-Hormonal tests:
FSH, LH, Prolactine and testosterone, all these hormones can be measured by blood tests
6- Examination of the Testes:
It is done if there is azoospermia (no sperms in the semen) to assess the ability of the testis to produce sperm in order to decide the way of treatment.
If there is obstruction in the seminal ducts, surgical intervention is done or the biopsy is done to use the sperms in ICSI ICSI (Intracytoplasmic sperm injection) procedures.
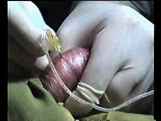
Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA)
-Vasography, if there is suspicion of seminal ducts obstruction.
-Test to diagnose varicocele (dilated tortuous veins around the testis).
-Doppler blood flow analysis.
-Thermograph.
7-Tests for disorders in ejaculation or in intercourse:
For example, urine analysis after ejaculation to check if there is retrograde ejaculation.
-Electric ejaculator.
8-Genetic and chromosomal tests:
-If there is suspicion of klinefelter’s syndrome or cystic fibrosis.
It is not necessary to do all the previous tests; the treating physician will decide which one is important for each individual case.
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
