Diagnosis Of Infertility In Women
Diagnosis of female infertility
Diagnostic Procedures
1-Hormonal levels:
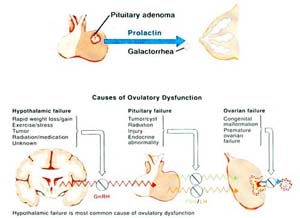
Importance of Hormonal tests
FSH, LH, testosterone and prolactine, the level of these hormones can be measured; the importance of measuring these hormones should be decided depending on the case of each patient for example testing progesterone level after ovulation to assess corpus Luteum function.
2- Vaginal Cytology:-
It is an old procedure in which a swab is taken from the vagina, and tested to get an idea about ovarian function, but it is not done any more and there is more advanced tests for ovarian function.
3-Testing Changes in the Cervix:
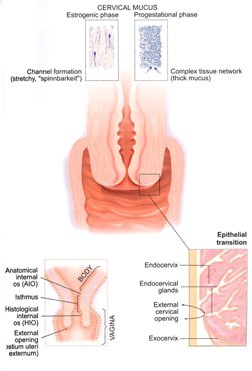
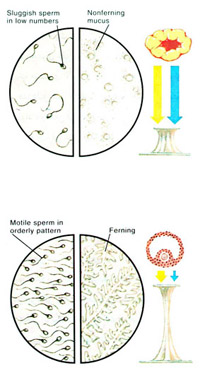
Cervical mucus has certain natural physiological changes that change during each cycle; this mucous is considered as a barrier against bacterial entrance to the uterus. During the first half of the cycle, cervical mucus is scanty, and thick, five days prior to ovulation it become watery and profuse, in order for the sperm to be able to pass through these secretions at the time of intercourse. Any change in these secretions, may impede or prevent sperm passage and consequently affect fertilization.
Hormonal changes during cycle each month plays a major role in these cervical changes (quality and amount), just before ovulation cervical mucus becomes watery and stretchable just like raw egg whites, 24 hour post ovulation, cervical mucus secretion stops, then it returns to be thick, white-yellow in color all through the second half of the cycle.
4-Microbiological, laboratory and blood tests:
For example :-Liver function test.
- Blood sugar level.
- Urine analysis.
- Other tests for contagious microorganisms.
5-Ultrasound examinations:
It is used to visualize internal organs including uterus, ovary, testes, prostate, liver, kidneys, and gallbladder……….etc, ultrasound is better than x-ray examination because it is not harmful for body tissues, and it can be used for men and women. There are two types of ultrasound in the diagnosis of female infertility:
A-Trans abdominal ultrasound:
In this type, the probe is used over different areas of the abdomen depending on the aim from the examination, in this case, mainly the uterus and both ovaries.
B-Trans-vaginal ultrasound:
It gives more obvious and clear image for the ovaries, so it is better for accurate measurement such as: measuring follicular size after ovulation induction by medications, diagnosis of PCOS and to check for ovulation, pelvic organs in general, endometrium, uterine wall (myometrium), and fibroids (benign uterine tumor) all these are diagnosed easier by vaginal ultrasound.
How often should ultrasound be done to check for ovulation?
Usually a primary examination at the second or third day period to check on the uterus ovary and diagnose PCOS, the second examination is done at day 13 of period to check follicular size and ovarian function whether during normal cycle or after induction of ovulation, usually if the woman is not taking any ovarian stimulant, the average follicular size is 12-14 mm, and it increases by 1-2 mm/day, if ovulation happened there are certain signs the treating physician can notice, on ultrasound.
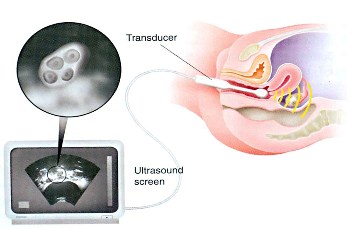
The size of the mature follicle suitable for fertilization depends on the type of treatment used for ovarian stimulation, usually the mature follicle is suitable for fertilization, but sometimes it might be obvious on ultrasound that it is mature but it is not suitable for fertilization, so the physician may need serial follow up with ultrasound because follicular growth may stop, or continue to grow without ovulation, in this case he will need to give HCG hormone to induce ovulation, if the follicle continues to grow, ovarian cyst (LUF) will develop, it is not a serious condition, it doesn’t need treatment and will resolve spontaneously.
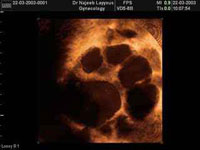
Ovarian Follicles as seen by Trans-vaginal ultrasound
Other conditions that may be diagnosed by ultrasound:
- Small immature ovary in a mature woman (hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism).
- Infantile uterus (small size uterus).
- Check endometrial thickness in different menstrual stages.
- Multi cystic ovaries: a condition similar to PCO, but the follicles on ultrasound are less in number and larger in size.
- Women with anorexia nervosa in the healing process.
- Diagnose uterine fibroids or ovarian masses.
- Diagnose early pregnancy.
- Congenital anomalies in the fetus.
- Diagnose multiple pregnancies (presence of two or more embryos).
- Check on fetal presentation (if the head is down in the lower part of uterus), placental location, and sex of the baby.
- Diagnose ectopic pregnancy.
- Dating of pregnancy, estimation of fetal weight, check on the amount of liquor.
Color Doppler ultrasound:
It is a modern device and its use in infertility diagnosis is still under research. It measures the blood flow in blood vessels, so it can measure the blood path between the ovaries and uterus.
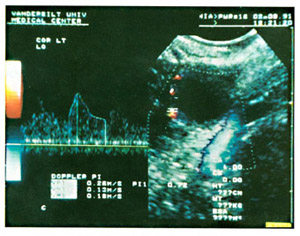
Color Doppler ultrasound
Can this method affect the follicle or harm it?
The answer is till now no proven harm for the follicles.
6-Hysterosalpingogram.(H.S.G)
In this method, colored material (dye) is introduced through a tube inserted in the cervix, then serial multiple x-ray pictures are taken to visualize the passage of the dye on the screen, if there is a blockage in the fallopian tube, there will be no passage of dye, it should be mentioned that the amount, and duration of dye injection does not cause harm.
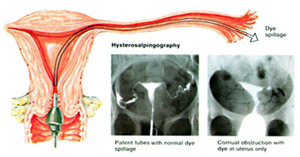
Hysterosalpingogram.(H.S.G)
This procedure does not cause annoying symptoms except some lower abdominal discomfort; it takes only a few minutes and doesn’t need hospital admission.
This procedure is helpful in the diagnosis of:
- Intrauterine lesions (fibroid, polyps).
- Tubal blockage or dilatation (hydrosalpinx).
- Uterine anomalies.
- Intrauterine adhesions (Asherman’s syndrome).
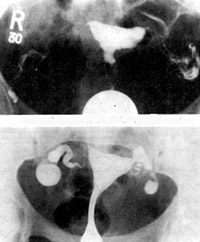
H.S.G Showing patent tubes
Tubal blockage and dilatation (hydrosalpinx).
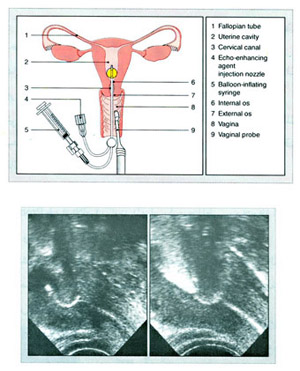
7-Hysterosalpingo Contrast Sonography (HY-CO-SY) :-
Since fallopian tubes can’t be visualized using ultrasound especially assessing their patency, this technique was developed, and it has many advantages.
- It is complementary to ultrasound examination which is becoming more widely spread and accepted in modern medicine.
- It avoids the patient's exposure to x-ray examination as in HSG.
- No need to use iodinated contrast media which might cause allergic reactions.
- Comparing HY-CO-SY to other techniques it is minimally invasive and it is not painful.
- No need for general anesthesia.
- It is an office procedure and doesn’t need hospitalization.
- It has quick and accurate results.
- It can give detailed information regarding structural and functional situations of the organ examined, if there are any anomalies.
For example, while examining the endometrial cavity, it can differentiate between submucosal fibroid and endometrial polyp.
This procedure can be done by either abdominal or transvaginal ultrasound.
First: Cleaning of the vulva (genital area), the woman is asked to bend her knees, and open them a little bit while she is lying flat on her back, the cervix is held using forceps, a catheter is inserted through the cervix, a special colored material called Echovist..200 is inserted through this catheter, it takes only 10-15 minute, and doesn’t need anesthesia as said before, at the end of the catheter there is a balloon that will be inflated in order to fix the catheter inside the uterus, before vaginal ultrasound is introduced inside the vagina, then the flow of the colored material is followed passing through the uterus, and both fallopian tubes on the screen, if there is obstruction in the tube the patient will feel some discomfort or mild pain, and she is asked to report that immediately to the doctor.
- The treating physician needs from 2-3 ml to visualize the uterus and identify abnormalities such as uterine septum or myoma (fibroid).
- To visualize the tubes, another 1-2 ml of the colored material is added to the total amount.
- At the end of the examination the balloon is deflated before removing the ultrasound probe, so that the doctor would be able to visualize any lesion that was hidden by the balloon.
- Very mild lower abdominal pain (dysmenorrheal like pain) might be felt, not more than one hour after the test, and it is easily managed by simple analgesia.
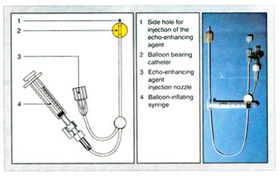
Hysterosalpingo Contrast Sonography
This procedure is:
- Quick.
- Easily done.
- No major side effects.
- The patient is comfortable while performing the procedure.
Some abnormal conditions that may be noticed:
- Reflection zone in the endometrium mostly due to previous caesarean section.
- Intrauterine adhesions like Asherman’s syndrome.
- Polyps.
- Fibroids
- Uterine anomalies like arcuate uterus, bicornuate uterus, Uterus duplex.
- Tubal occlusions.
If it is bilateral, the uterus will become swollen on ultrasound screen and mild pain may be felt, if it is unilateral, there will be no swelling of the uterus and the blocked tube and the site of the blockage will be obvious on the screen.
Adhesions or tumors will cause more time for the dye to pass; with no enough experience it will cause misdiagnosis.
10- Falloposcopy:-
Either during laparoscopy or transcervical with or without hysteroscopy.
11-P.C.T (post coital test):
Cervical mucus becomes watery at the time of ovulation, stretchable, transparent and in profuse amount, in order to allow the sperm to pass and fertilization be done, in this test cervical sample is taken 6-10 hours post coitus and examined under the microscope to assess functional ability of the sperm and cervical mucus elasticity.
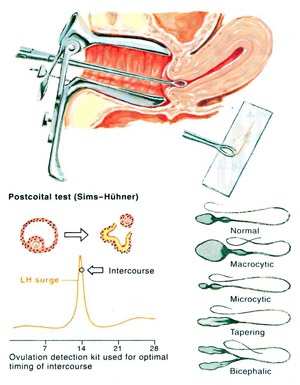
At the time of ovulation, cervical mucus becomes watery, stretchable, transparent and in profuse amount, in order to allow the sperm to Cervical Causes of Infertility in Womenpass and fertilization be done, in this test cervical sample is taken 6-10 hours post coitus and examined under the microscope to assess functional ability of the sperm and cervical mucus elasticity.
Mucous secreting cells in the cervix are under the effect of estrogen which is produced in large amounts around the time of ovulation, at this time, 98% of the mucous is water resulting in increased elasticity, it also contains some materials at the time of ovulation due to increased amount of salts and water that interact with the protein in cervical mucus, which is indirect evidence for increased in estrogen level, all the above mentioned changes help to maintain the sperms for 24-48 hours post ovulation, progesterone level increase causing the mucous to lose its elasticity and decrease the maintenance of sperms, in this test if we could see 15-20 sperm it is considered a good result, if the count is less than five, it indicates a weak potential for fertility.
Post coital test is an easy test; in addition, seminal fluid analysis will help to give more clear idea about the best way for infertility treatment.
It was noticed that the amount of cervical mucus can compensate some shortage in semen amount.
Post coital test is an easy test as said before, but it is not that reliable, sometimes it can give false negative results such as in the presence of antibodies in the cervix, or if there is severe infection in cervical mucus this will affect the sperms and give bad result in P.C.T though the seminal fluid analysis is good.
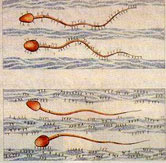
Post coital test showing active motile sperm
Assessment in P.C.T Post coital test includes:
1 - Elastity of the mucous since sperm cannot pass through if it is very thick.
2 - Presence of antibodies: Uterine cervix has the highest ability to produce antibodies followed by endometrium, fallopian tube and green fluid which gives local immunity, so the presence of sperm will cause sperm antibodies and consequently antibodies in the serum.
Uterine cervix is covered with plasma cells and it also contains the proteins required for antibodies formation. These contents differ in their amount, in different times of each menstrual cycle. It becomes less around the time of ovulation.
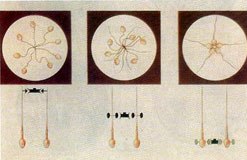
Sperm Antibodies
3 - Determine if sperms are able to reach the cervix or not.
4 - Presence of vaginal or intrauterine infections, or if there is bacterial, fungal or other pathological microorganisms.
12-Endometrial Biopsy:
It is done at day 21-23 of cycle. First, dilation of uterine cervix then curetting of the endometrium, then it is sent for histopathology, if ovulation happens, serum progesterone level will be within certain range that correlates with histopathology result. If ovulation did not happen, there will be low progesterone serum level and different histopathological results.
Although some medical centers still use this method, to check for ovulation and assess fertility but with scientific and technical advances in the medical field, and with the presence of vaginal ultrasound, which can help in this issue, this test has become less and less important as it was before.
13 -Basal Body Temperature Chart (B.B.T):-
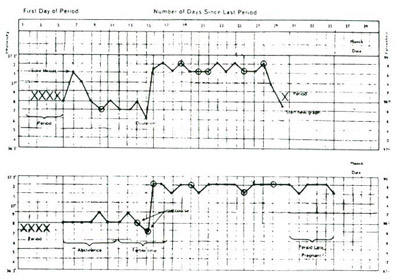
It depends on measuring body temperature daily, once, early in the morning, starting from the first day period and document this temperature on a chart daily, till the time of the next period. If there was ovulation, a small increase in temperature (0.5-1.25c) will be noticed at the second half of period, which is caused by increased level of progesterone and it stays higher, till the first day of the next cycle or one day before it returns to its lower level. If pregnancy happens, it stays higher. If there is no ovulation, the temperature stays the same all through the cycle.
This method is inaccurate for many reasons. Body temperature readings might be wrong or taken incorrectly. The woman might have a high temperature due to infection or any other disease or there may be irregular patterns of increased and decreased temperature (step wise rise). In addition, the woman may have irregularities in her hormones though ovulation happens. In this case, changes in body temperature will not be ideal as in day 12-14 from cycle.
Other reasons for inaccuracy are different body reactions to hormonal changes i.e. high level of progesterone with ovulation but it does not cause increase in temperature.
Due to all the above mentioned causes, and recent advances, this method is not used frequently.
14-Immunological tests:
- Anti sperm antibodies either in serum or cervical mucus.
- Ovarian antibodies in cases of premature ovarian failure.
- Other antibodies like anti-phospholipid antibody which plays an important role in the ability to conceive after embryo transfer.
15-Genetic and chromosomal tests:
Such as in the cases of:
1-Premature ovarian failure.
2-Primary amenorrhea (menstruation cycles never starting).
3-Recurrent abortions.
16-Psychological tests:
Due to its major effect on fertility. See stress and infertility
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
