Treatment of infertility | Treatment of female infertility | Treatment of Male infertility
After diagnosis for the cause of infertility; either due to male or female factor, treatment would be according to the diagnosis.
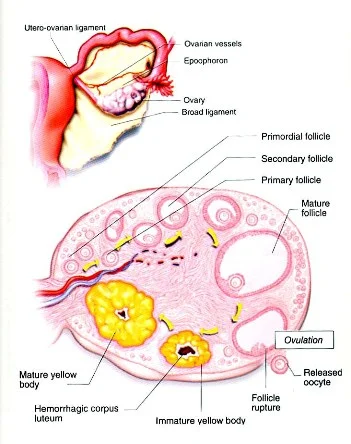
Treatment of female infertility:
A- Medical Treatment of female infertility:
It depends on the diagnosis, some women may need hormonal therapy; others need other treatments such as endometriosis. Most of the cases will need hormonal therapy by giving different kinds of hormones to stimulate the ovary in order to enhance follicular growth (controlled ovarian stimulation either oral pills, injections or both such as FSH, tamoxifen, clomiphene citrate, GNRH analogues, antagonist, HMG), these medications help also in controlling the time of ovulation so that the possibility of fertilization at the proper time will be higher.
At First, one of the previous medications would be given in certain amount, and duration decided by the treating physician, follicular tracing and follow up is done either by using ultrasound, hormonal level or both, when the number and the size of follicles are appropriate, HCG hormone will be given by intramuscular injection with timing of intercourse, it should be mentioned here that, these medications don't increase the incidence of congenital fetal anomalies or recurrent abortions, but the incidence of multiple gestation (more than one fetus) would be higher
Women who need induction of ovulation more are:
-Women with hormonal disturbances.
-Women with Polycystic Ovary Disease (PCOs).
B-Surgical treatment for female infertility:
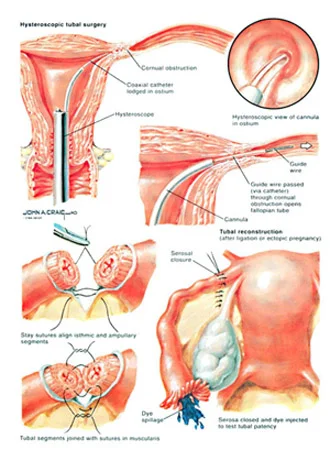
- For example, treatment of fallopian tube blockage either by trying to treat the blockage, or by using in vitro fertilization (it would be explained later), also in cases of endometriosis, surgical intervention might be needed in addition to medical treatment, or the need for surgical intervention if there is fibroids impeding pregnancy:
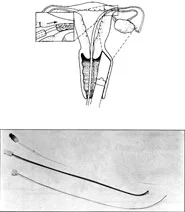
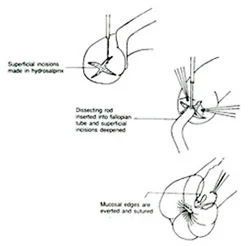
- -If there is part of the tube that is blocked it can be removed and reanastomosis of the remaining parts done, if the blockage is at the distal part of the tube, the tube would become swollen which is called hydrosalpinx, a surgery known as salpingostomy can be done.
- -If the blockage is at the area where the tube is attached to the uterus and the blockage is extended to the uterus, the whole blocked area is removed followed by reanastomosis to the close open area; this surgery is called (tubal reimplantation).
- -Reopening the blocked tube can be done using a special catheter inserted through the cervix and uterus to reach the blocked area of the tube and reopen it, this procedure is called (transcervical selective salpingograph) which is diagnostic and therapeutic approach to cases of proximal tubal injection failure.
- The catheter used is a rubber catheter with a guide wire that helps in insertion, then the guide wire is removed, and the catheter is inserted through the ostium transcervical selective salpingograph(the area where the tube is attached to the uterus) when it reaches the obstructed area, the catheter is moved in certain way to bypass the obstruction, then the colored dye is injected to make sure that there is no blockage, and the tube is patent.
- This procedure has good results with minimal side effects in very short time with a success rate of 75.3%.
- -If fibroids are thought to be the only cause for infertility, surgical removal of these fibroids can be done by laparatomy (abdominal incision) or by laparoscopy.
- -Uterine septum, intrauterine adhesions and intrauterine fibroid are removed by hysteroscopy.
- -Ovarian drilling is done for women with Polycystic Ovary Disease PCO.
- -The success for any previous surgery will depend on the proper diagnosis and the skill of the surgeon.
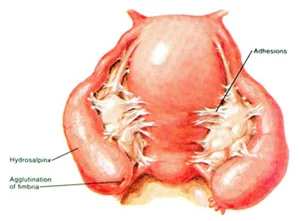
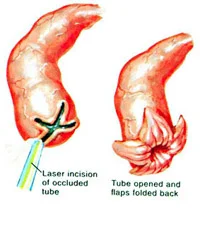

C-Other causes of female infertility such as Sperm antibodies inside female body, increase thickness of cervical mucus and other different causes that are less frequent causes are treated accordingly.
D-Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
Treatment of male infertility:
Find the cause and treat it.
1-Instructions to increase sperm number and improve its quality:
A-Changing lifestyle:
- Quit smoking.
- Avoid excess alcohol intake.
- Avoid exposure to sources of high temperature.
- Avoid wearing tight underwear’s.
B-Changing environment:
- Avoid exposure to some chemical substances such as, working in industries.
- Stop medications that affect sperms.
2-Treatment that increase sperms production and its function:
A-Medical treatment:
1-Hormonal treatment:
- To increase sperm production such as, Tamoxifene, Clomiphene, Androgens, Bromocriptine, GNRH and gonadotrophins.
- GNRH and Gonadotrophins give excellent results in cases of hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism.
2-Other treatments:
- Zinc, Phosphodiesterase inhibitors like, Pentoxifylline, and Kallikren are used to try to improve sperm motility, the response is limited and it differs from one male to another.
- Antibiotics to treat chronic genital tract infections.
- Other treatments like, vitamins didn’t show promising results.
B-Surgical treatment for male infertility:
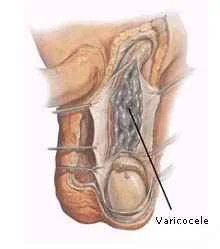
Surgery done to treat varicocele. Varicocele alone is not by itself a reason for surgical intervention. Many fertile men have varicocele, and the success rate for varicocele surgery to improve sperms quality is still controversial, some studies showed promising results others did not.
3-Repairing the path of sperm to Oocyte:
Reconnecting spermatic cord (vasovasostomy).
The earlier the diagnosis is made and surgical intervention performed, the better are the results because the delay may result in anti sperm antibody production.
- Fixing epididymal obstruction (vasoepididymostomy), either the obstruction is congenital or due to infection.
- Using synthetic vesicle to collect semen in cases of absent spermatic cord.
- Aspiration of sperms from epididymus (MESA) or from testis (TESE or PESA) and using it in ICSI procedures (it will be mentioned later).
4-Treating Erectile Dysfunction if it was the cause for infertility:
A-Medical treatment for erectile dysfunction:
- Injecting the penis with certain substances such as, prostaglandins.
- Medical treatment for hyperprolactinemia (high prolactine hormone level) such as bromocriptine.
- Androgen in cases with low testosterone level.
- Treating medical conditions affecting erection such as diabetes, thyroid problems, epilepsy.
B-Surgical treatment for erectile dysfunction:
- Surgery done to the arteries supplying the penis to increase the amount of blood reaching the penis in cases of diseases affecting arteries such as, diabetes or smoking.
- Using certain devices to induce erection (like vacuum devices).
- Inserting plastic penis inside the penis.
- Electric ejaculator that will stimulate the nerves responsible for ejaculation via localized small electric current, to obtain semen that will be used in IUI, IVF or ICSI.
C-Psychological therapy for erectile dysfunction: When it is the cause.
5-Treatment of ejaculatory problems:
A-Premature ejaculation.
B-Treatment of failure of ejaculation according to the cause, or by electric ejaculator.
C-Retrograde ejaculation is treated according to its cause:
- Medical treatment such as, using Alpha-Sympathomimetic Agents.
- Using sperms present in urine for ICSI procedure after preparing it in the lab.
- Electric ejaculator.
- Surgical correction for the valve dysfunction to prevents retrograde ejaculation.
6-IUI (intrauterine insemination).
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
