Varicocele Effect on Infertility and its Management
The Varicocele is the widening and dilatation of the veins around the spermatic cord inside the scrotum, usually on left side.
It affects around 15-20% of the masculine general population, most of them are fertile with normal semen analyzer and affect 20 to 40% of infertile men.
Symptoms of varicocele
- Asymptomatic.
- Dull discomfort.
- Heaviness in scrotum that increase while sitting and standing and worsen over the day and it can only be relieved by lying on the back.
- Feeling a lump or swelling in the scrotum.
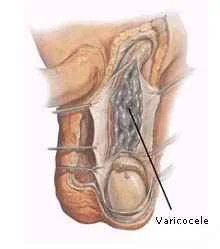
The pathophysiology of varicocele and its effect on fertility
- The dilation of the veins draining the blood from testicles due to abnormality in the venous valves, most commonly the left side. The blood flow in those dilated vessels cause extra heat on the testicles, which may affect sperms production and quality.
- The intratesticular pressure and reduces the blood flow that may lead to Hypoxia and reflux of toxic metabolites from adrenal gland.
- This may damage the DNA in the sperm head due to oxidative stress.
- New studies are now showing that varicocele repair improves semen fluid analysis parameters (count and motility), but few studies showed improvement of pregnancy rate.
However, those results were confirmed both for fertile and infertile men having Varicocele, so it is difficult to link between it and fertility status.
The improvement of semen fluid analysis parameters is usually seen during the first 3-6 months of surgery.
The decision of intervention is based on specific criteria, in which the physician should assure the following;
1- Pain and discomfort
Or
2- Infertility more than 2 years with all the following
- Normal female partner
- Abnormal semen analysis
- Palpable varicocele by clinical examination
Or
3- Adolescents with progressive failure of testis formation
Varicocele is diagnosed by physical examination by an obstetrics and gynecology specialist, expert in male infertility or by a urologist.
It is described as a “bag of warms”.
Varicocele found only during scrotal ultrasound examination is not an indication for intervention.
Scrotal ultrasound is used to rule out causes of varicocele and other causes of pain and discomfort.
Daily habits and lifestyle such as smoking predispose patients to more severe damage from a varicocele.
Grades of varicocele
Grade 1 It is not felt by the patient himself. Found by doctor’s exam during Valsalva maneuver.
Grade 2 It is not felt by patient but found by the doctor’s clinical examination.
Grade 3 It is visible.
Treatment of varicocele
Pain can be managed by pain killers such as NSAID and tight underwear.
As mentioned before in some conditions varicocele may need surgery
In which the blood will stop flowing in the swollen veins and this leads to a decrease in the heat affecting the testicles.
Types of surgical interventions
- Open surgery: Usually it is outpatient operation, under general or local anesthesia through a small incision in the groin.
- Microsurgery: microscope can be used.
- Laparoscopic surgery; this require general anesthesia.
- Percutaneous embolization this can be done under local anesthesia.
Complications
- Infection
- Hemorrhage
- Blood clots.
- Hydrocele (collection of fluids in the scrotum).
- Testicular atrophy.
(Scrotum is the sac holding the testicles).
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
