Pregnancy and Amniocentesis
There are many problems that might exist in the fetus, which appear in the fetus on ultrasound as a problem in the growth (the measurements are smaller) or structural abnormalities or fluid collection behind fetal neck. There are hereditary / genetic problems that do not give signs on ultrasound and are discovered after birth. The technique of examining the amniotic fluid (amniocentesis) enables us to diagnose many chromosomal/genetic problems in the fetus while it is inside the mother’s womb.
Accordingly, the fetus can be treated, the pregnancy terminated, or preparation for postpartum care by providing an NICU bed and pediatric care that the fetus might need according to the case.
The test can detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, Tay-Sachs disease, muscular dystrophy, and spina bifida. Drugs.com states that amniocentesis is often recommended for pregnant women over age 35, and for women who have an abnormal “triple screen” blood test during pregnancy.
It is also possible to analyze Amniotic fluid to search for possible infections inside the uterus to give the necessary antibiotic treatment before a miscarriage or premature birth occurs.
the fluid can also be examined to ensure the maturity of the fetal lung (in cases of premature birth).
In cases of rhesus disease, the amniotic fluid is analyzed to estimate the presence of anemia in the fetus and to determine the need for a blood transfusion for the fetus inside the uterus.
there are cases of high amniotic fluid pressure inside the uterus that requires withdrawal of the fluid to reduce the pressure (which improves the patient’s breathing and prevents premature birth).
Amniotic fluid examination is a diagnostic test that is performed during pregnancy to obtain a small sample of the amniotic fluid that surrounds the fetus, it is a simple procedure through which we can examine the genetic material (DNA) of the fetus between 15-20 weeks of pregnancy, as follows:
** Under sterile conditions, the abdomen is sterilized, a numbing material is inserted to minimize discomfort, a needle is inserted through the abdominal wall into the uterus under ultrasound guidance, and a sample of the fluid surrounding the fetus (20 ml) is withdrawn. The procedure is under control and direct vision with an ultrasound device, and then the sample is sent to the laboratory where the sample contains cells from the fetus with fetal DNA, and they are studied in search of chromosomal abnormalities or genetic defects, depending on the case, and in some cases to diagnose the presence of infections inside the uterus.
The mother can return to her normal life immediately after the examination.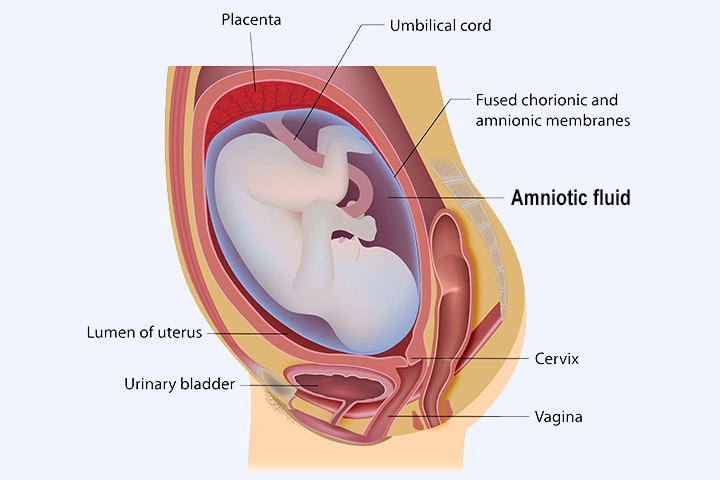
Obtaining results may be within 24-48 hours, and it may take a longer period, depending on the technique used.
What are the contraindications for an examination?
1- The presence of a viral infection in the
mother (hepatitis C, HIV) for fear of transmitting
the infection to the fetus
2- The mother has a tendency to bleed
(bleeding diathesis) or is actively bleeding
4- The presence of contractions in the uterus
or signs of infection inside the uterus.
What are the possible complications?
It is an invasive procedure and carries risks for both the mother and fetus
1- Premature birth
2- Placental abruption
3- Miscarriage (pregnancy loss), The risk of miscarriage is about 1 in 400 to 500 procedures.
4- The occurrence of infections inside the
uterus
5- Increasing the proportion of antibodies in
cases of rhesus disease
6- Twisting of the limbs of the fetus due to the
withdrawal of an excessive amount of fluid
Who should do the operation? A person who is properly trained and familiar with the technique and its complications.
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
